

Identify that alga:
Web-based key to genera - 21: sheathed blue-green colonies and coenobia
Algal Search Sitemap and quick links |
|||||||
Jump to: (filename) |
unbranched cyanobacteria (search5) |
branched cyanobacteria (search6) |
|||||
attached, flat plate (search13) |
|||||||
Colonies and coenobia : Cyanobacteria (search21) |
|||||||
Unicells (under development) |
non-flagellate cells without case (under development) |
in silica case = diatoms (under development) |
flagellate cells (under development) |
||||
no chloroplast: |
|||||||
Click on the underlined text link to jump to the next step
| Cyanobacterial colonies and coenobia | |||||
| Click on the thumbnail for a larger image | |||||
| planktonic, with sheath | |||||
|
|
|||||
| coenobia: | INFORMATION: cell number in a geometric series: 2,4,8,16,32, etc. | ||||
|
 |
||||
|
 Merismopedia |
||||
|
 Eucapsis |
||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
| Colony: composed of an indeterminate number of cells | |||||
colony spherical or subspherical: |
|||||
|
  Gomphosphaeria |
||||
|
  Snowella |
||||
|
 Woronichinia: compare carefully with Coelosphaerium |
||||
|
Coelosphaerium |
||||
|
|||||
|
 Aphanocapsa |
||||
|
|||||
|
  ? Aphanothece |
||||
|
|
|||||
in A. stagnina, some cells may have individual sheaths |
|||||
|
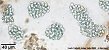 Microcystis |
||||
Microcystis aeruginosa: |
|||||
usually with outer margin of mucilage cell-free;
mean cell diameter ~6µm. |
|||||
|
Microcystis flos-aquae: |
  |
||||
without cell-free outer margin of mucilage;
mean cell diameter ~3.5µm. |
|||||
Colony a flat plate, cells not arranged in a regular pattern (cf. Merismopedia)
|
 Microcrocis |
||||
cells form filaments enclosed in a tough mucilage envelope; heterocysts present
|
 Nostoc |
||||
Colony is a rosette of radiating tapering filaments, each with a heterocyst at the base and a sheath.
|
 Gloeotrichia |
||||
| Genera not included: | Chroococcopsis, Gloeothece, Hydrococcus, Rhabdogloea, Xenococcus | ||||
John Kinross